D.R. McNatty & Associates, Inc. actively monitors trends and emerging technologies within project-focused industries to identify developments that will impact and create new opportunities for project management and control professionals. By staying at the forefront of industry advancements, we ensure our clients are equipped with innovative solutions to meet evolving challenges and achieve project success.
The global push for cleaner energy has sparked innovation across the energy sector. Among these breakthroughs, mini nuclear reactors, also known as Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), are emerging as a promising solution to meet growing energy demands sustainably. Compact, flexible, and efficient, SMRs represent a revolutionary approach to nuclear energy, offering several advantages over traditional large-scale reactors.
What Are Mini Nuclear Reactors?
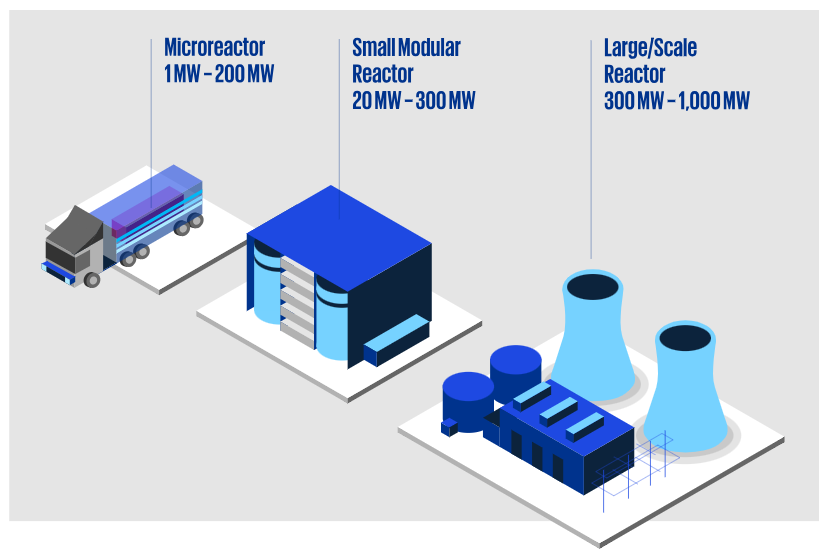
Mini nuclear reactors are a new class of nuclear reactors designed to be smaller, safer, and more adaptable than their traditional counterparts. With power outputs ranging from a few megawatts to hundreds of megawatts, SMRs can serve smaller grids, remote communities, and industrial applications. Unlike large nuclear plants, which are constructed on-site, SMRs are typically factory-built and shipped to the site for installation, reducing construction time and costs.
The Case for SMRs in the Clean Energy Transition
- Reduced Carbon Emissions
Nuclear power is a zero-carbon energy source during operation, making it a critical tool in the fight against climate change. SMRs have the potential to provide consistent, carbon-free electricity, complementing intermittent renewable sources. - Enhanced Safety Features
Advances in SMR technology incorporate passive safety systems that rely on natural processes, such as gravity and convection, to cool the reactor without human intervention or external power. This reduces the risk of catastrophic failures, making SMRs safer than older reactor designs. - Cost-Effectiveness
The modular design of SMRs allows for mass production in controlled factory environments, significantly reducing construction costs and timelines. This scalability makes SMRs an attractive option for developing nations and communities with limited infrastructure. - Flexibility and Scalability
SMRs can operate independently or in clusters, providing flexibility to match energy output with demand. This adaptability makes them ideal for a variety of applications, from powering small towns to providing process heat for industrial operations. - Energy Security
SMRs can be deployed in remote locations, providing a reliable and sustainable energy source for regions that currently rely on diesel generators or have limited access to energy.
Challenges to Overcome
While SMRs hold significant promise, their widespread adoption faces several hurdles:
- Regulatory Framework: Existing nuclear regulations are tailored to large reactors, creating challenges for the certification and deployment of SMRs.
- Public Perception: Misinformation and fear surrounding nuclear energy remain barriers to public acceptance.
- Waste Management: Though SMRs produce less nuclear waste than traditional reactors, developing long-term storage solutions is critical.
- High Initial Costs: Despite cost-saving designs, the upfront investment required for research, development, and infrastructure remains substantial.
Global Adoption and Key Players
Several countries and companies are leading the charge in SMR development:
- United States: Companies like NuScale Power and Kairos Power are pioneering SMR designs, to power companies such as Microsoft and Google, with plans for commercial deployment by the late 2020s.
- Canada: Canada is investing in SMRs as part of its clean energy strategy, focusing on deployment in remote and Indigenous communities.
- United Kingdom: Rolls-Royce is developing SMRs to replace aging nuclear plants and support net-zero goals.
- China: China is considered one of the most advanced countries in SMR development, with projects like the HTR-PM, a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor, already in operation.
The Path Forward
To realize the full potential of mini nuclear reactors, governments, industries, and researchers must collaborate to:
- Streamline regulatory processes for SMR deployment.
- Invest in public education campaigns to build trust in nuclear energy.
- Accelerate research into waste management and recycling technologies.
- Provide financial incentives and subsidies to offset initial costs.
Mini nuclear reactors are poised to play a crucial role in the clean energy landscape. By offering a reliable, scalable, and low-carbon energy source, SMRs could bridge the gap between renewable energy ambitions and practical energy needs. As the world races to achieve net-zero emissions, embracing innovative technologies like SMRs will be essential to building a sustainable future.